railway-international.com
11
'24
Written on Modified on
TALGO: ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING, AN INCREASINGLY IMPORTANT COG IN THE SUSTAINABILITY CHAIN
Through additive manufacturing, Talgo has managed to create new designs that allow greater customization, the use of complex organic geometries and topological optimizations.
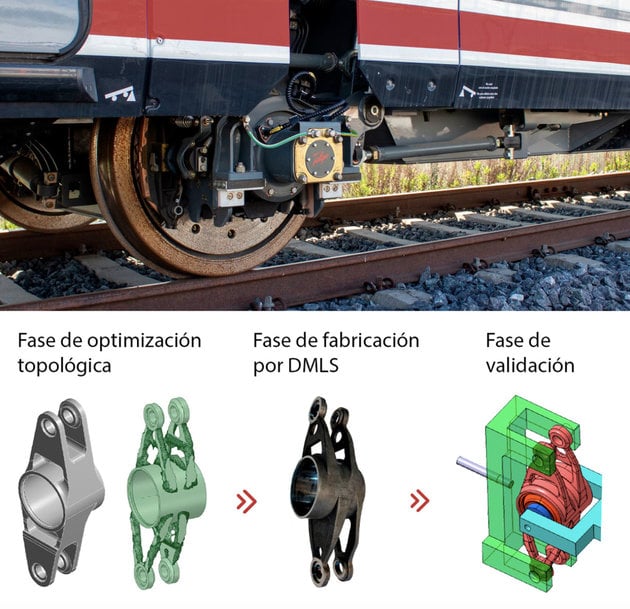
Additive manufacturing, one of the pillars of industry 4.0, is a new concept of production using 3D printing, without the need to use molds or tools. The extension of its use could shorten the transition towards a circular and more sustainable economy, since it would reduce supply chains and the material used for manufacturing, in addition to facilitating the recycling of excess material. At Talgo, thanks to a multidisciplinary group from different areas of the company that is dedicated to researching, analyzing, developing and integrating additive manufacturing solutions, the development of these parts covers most of the stages of the life cycle of its products, with the aim of optimizing the efficiency, quality and sustainability of the company's rolling stock.
Through additive manufacturing, the rolling stock manufacturer has managed to create new designs that allow greater customization, the use of complex organic geometries and topological optimizations. In addition, times within projects have been reduced thanks to rapid prototyping and Lead Time times have been shortened, the time that elapses between when an order is generated until the merchandise is delivered. Advances in additive manufacturing have also made it possible to reduce storage costs, since the company has a digital repository that allows the part to be manufactured at the destination.
Additive manufacturing throughout the life cycle of Talgo products
The parts produced using this technique cover the product design phase and extend to its implementation and maintenance. In the design and development phase, this technology is used to create prototypes and mockups to visualize and refine solutions before mass production.
Only when the parts have been validated are they implemented as a final product or as tooling with which to significantly improve assembly times and operational efficiency, since these parts are designed and intended to be ergonomic and easy to manipulate.
Regarding maintenance, the philosophy carried out from the beginning is to design easily replaceable and optimized parts to extend their life, thereby reducing downtime to a minimum. Furthermore, in response to the obsolescence of some parts, a reverse engineering process has been carried out by the Talgo additive manufacturing community (use of technologies such as 3D scanners, capable of analyzing and reproducing existing parts with a high level of detail and precision), for replacement.
Sustainability always on the horizon
Sustainability and the environment are always two aspects taken into account at Talgo. Therefore, the materials used in additive manufacturing are, in a very high percentage, recyclable and even biodegradable.
Depending on where you want to apply it, you can use metallic materials (steel, aluminium, titanium, nickel alloys, etc.) or polymeric materials (polyamides, polycarbonates, PLA, PETG, etc., most of them combinable with carbon fibers). , ceramics and glass to improve their properties). The choice of one or the other will be determined by the technical requirements, the relationship between cost and functionality and production management, although one of the objectives of the multidisciplinary group is to carry out powerful filtering that restricts the number of options as much as possible without give up mechanical, chemical, cost and compliance with current regulations.
Talgo and its additive manufacturing community are constantly researching and evaluating new materials and technologies that can offer significant benefits in terms of performance, durability and sustainability in all its products.
www.talgo.com

